What Is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
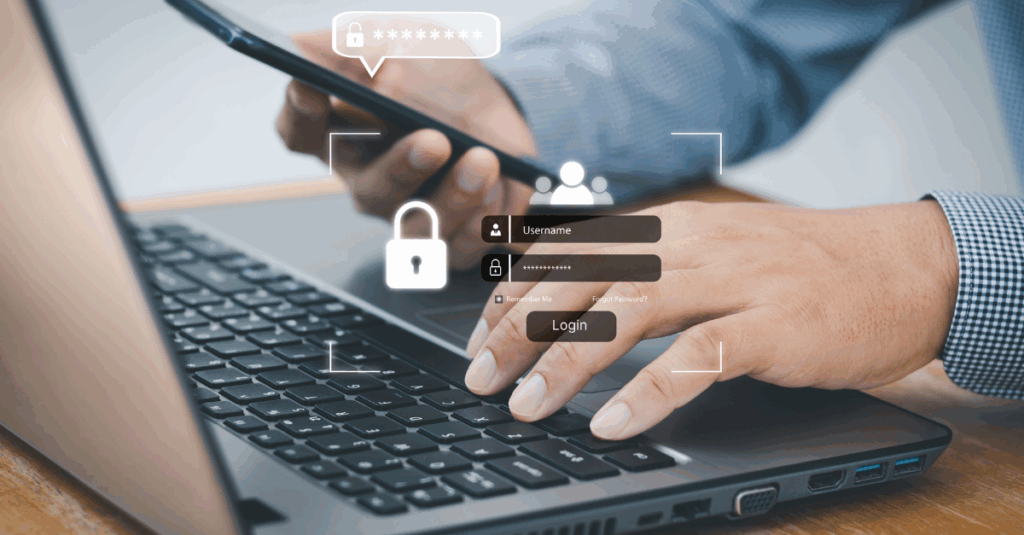
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource. These factors typically include something the user knows (password), something the user has (smartphone or security token), and something the user is (biometrics).
MFA plays a critical role in preventing unauthorized access to systems and data. It’s particularly effective against phishing attacks and brute-force attacks because it introduces multiple layers of defense.
Companies implementing robust email security strategies like those used by CMIT Solutions of Bothell and Renton have made MFA a foundational element in their defense strategy.
Why Do Businesses Use MFA?
MFA offers significant benefits that extend beyond just account protection:
- Enhanced security: Even if a password is compromised, additional verification prevents unauthorized access.
- Regulatory compliance: MFA supports compliance with HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and other frameworks.
- Reduced attack surface: Limits the impact of password-related attacks.
These benefits are especially crucial for businesses that handle sensitive information or operate in regulated industries.
Incorporating endpoint protection through solutions like advanced EDR adds another layer to your security model when used alongside MFA.
What Is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust is a security framework that assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default. It requires verification at every stage of digital interaction—“never trust, always verify.”
Core principles include:
- Least privilege access: Users only get access to what they need.
- Micro-segmentation: Limits movement within networks.
- Continuous monitoring: Tracks all activities and behaviors.
Organizations seeking comprehensive protection in the cloud era turn to Zero Trust models like those adopted by CMIT Solutions.
Why Is Zero Trust Becoming the Norm?
As remote work and hybrid teams grow, so do the number of access points and potential vulnerabilities. Zero Trust is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
Driving Factors:
- Remote access: More devices and users connecting from outside the office.
- Cloud adoption: Data is spread across various services and platforms.
- Evolving threats: Cyberattacks are more sophisticated and frequent.
Implementing multi-layered security helps enforce Zero Trust principles, as seen in this approach to network protection.
From MFA to Zero Trust: Bridging the Gap
While MFA and Zero Trust can function independently, they’re most effective together. MFA provides strong authentication, while Zero Trust controls access and verifies all interactions continuously.
When used as complementary solutions, they:
- Protect identities and endpoints
- Reduce lateral movement of threats
- Improve compliance and visibility
SIEM tools such as Microsoft Sentinel, used by CMIT Solutions, help bridge this gap by providing real-time insights into threats and anomalies.
What If You Don’t Evolve?
Failing to adopt modern security frameworks can have severe consequences:
- Data breaches: Single-point-of-failure credentials are easily exploited.
- Downtime: Malware or ransomware attacks can halt operations.
- Reputation loss: Customers lose trust in insecure organizations.
A reliable disaster recovery plan like this ensures you stay operational even during a security incident.
How to Start Transitioning
Implementing MFA and Zero Trust doesn’t happen overnight, but it starts with clear steps:
- Audit access controls and determine high-risk users and endpoints
- Deploy MFA for all users and sensitive services
- Segment networks and limit access
- Implement endpoint monitoring
- Choose trusted MSP partners for ongoing support
Solutions like Intune MDM offer streamlined device management that supports Zero Trust enforcement. This guide explains how to get started.
Why SMBs Need Managed IT Services
Many small businesses lack the resources or expertise to manage a full Zero Trust model on their own. That’s where proactive IT support and managed services become vital.
Benefits include:
- 24/7 monitoring and threat detection
- Automatic patching and software updates
- Helpdesk support for security configuration
CMIT Solutions helps small businesses in Bothell and Renton integrate modern security with day-to-day operations.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity has entered a new era where single sign-on and perimeter-based models are no longer enough. Multi-Factor Authentication and Zero Trust are the new benchmarks. Whether you’re just beginning or advancing your strategy, combining both will help secure your business in an ever-evolving digital world.
Consider working with a managed partner like CMIT to ensure compliance, resilience, and long-term value. If your team also collaborates remotely, unified communication tools can further strengthen identity and access control measures.
Stay secure, stay compliant, and stay ahead.