In this managed services report, you’ll find best practices for MSPs drawn from research and interviews with top industry experts. Discover what’s working well for MSPs and get actionable advice that you can use to improve your own managed services business.
SOC2 Compliance
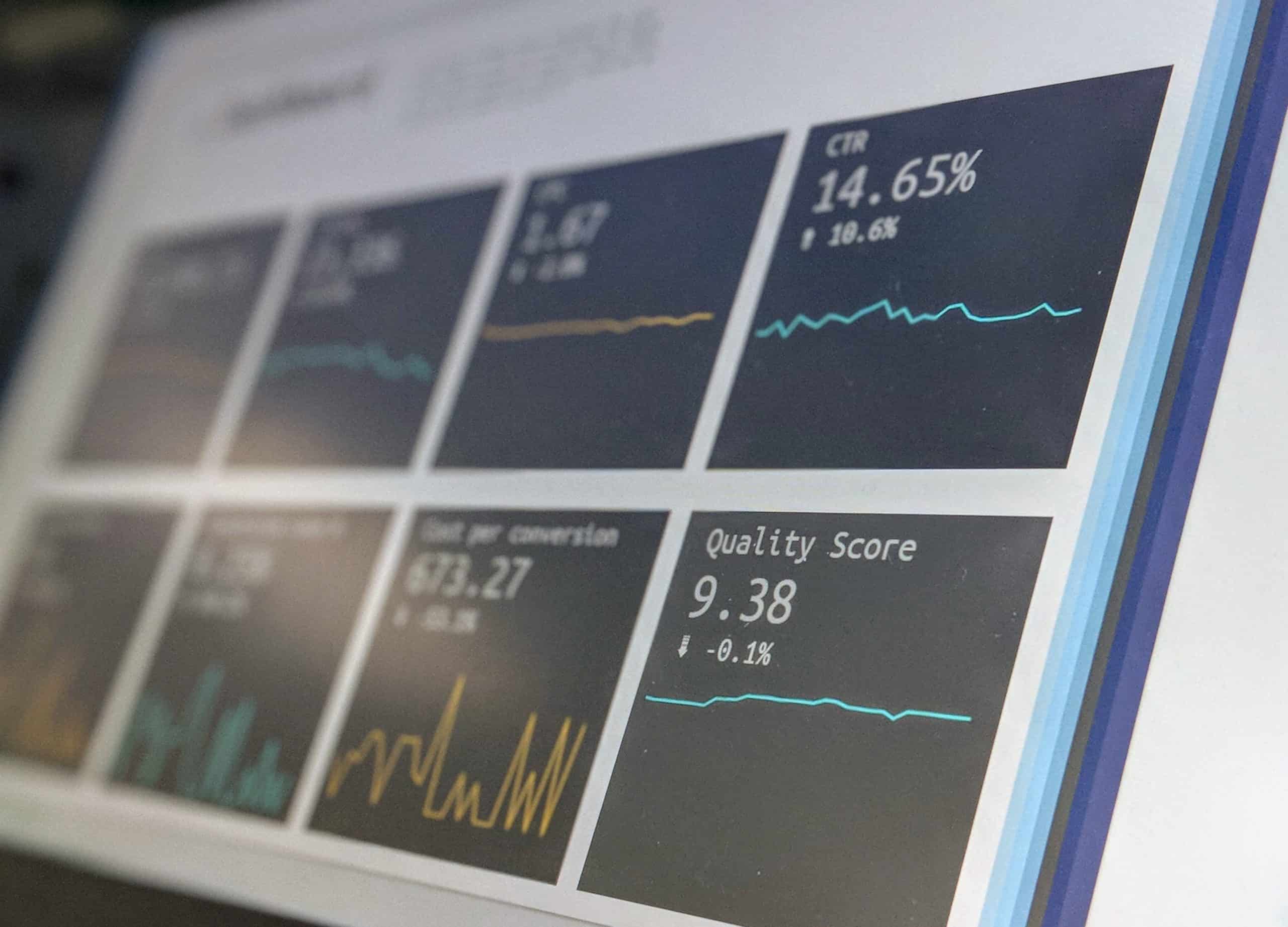
The term “SOC” stands for “Security Operations Center.” A SOC is a physical or virtual location from which an organization monitors and responds to security events. SOCs are becoming increasingly important as organizations face more sophisticated and targeted cyberattacks.
There are many different best practices that can be followed when setting up and running a SOC. Here are some of the most important:
Establish clear goals and objectives for the SOC. What does the SOC need to achieve? How will it be measured?
Define the scope of the SOC. What systems and data will be monitored? Who will have access to the SOC?
Develop policies and procedures for the SOC. What processes will be followed when an incident is detected? Who needs to be notified?
Build a team of skilled and experienced security professionals. The team should have a mix of technical, analytical, and communications skills.
invest in the right tools and technologies. The SOC should have access to the latest security intelligence, including threat data, malware signatures, and vulnerabilities.
Test the SOC regularly. Regular testing will help to ensure that the SOC is functioning properly and that incident response procedures are effective.
Named Accounts And Multi-Factor Authentication
The blog section for “MSP Best Practices: A Managed Services Report” covers the topic of named accounts and multi-factor authentication. In managed services, it is essential to have tight security measures in place to protect client data. One way to do this is through the use of named accounts and multi-factor authentication.
Named accounts are specific to an individual user and can be used to track and control access to sensitive information. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more pieces of evidence to verify their identity.
MSPs have a duty to their clients to ensure the security of their networks and data. One way to do this is to ensure compliance with SOC 2 Type II standards.
SOC 2 Type II compliance is a set of standards that define how businesses should manage their information security. MSPs that are compliant with SOC 2 Type II standards have been audited by an independent third-party and have been found to meet all of the requirements.
MSPs that are compliant with SOC 2 Type II standards can provide their clients with peace of mind knowing that their networks and data are secure. In addition, MSPs that are compliant with SOC 2 Type II standards can market themselves as being able to provide a higher level of security for their clients.
If you are an MSP that is looking to become compliant with SOC 2 Type II standards, there are a few things you need to do. First, you will need to have your policies and procedures audited by an independent third-party. Second, you will need to implement the recommendations from the audit report. And finally, you will need to have your compliance verified by the independent third-party on an annual basis.
Becoming compliant with SOC 2 Type
When used together, these two security measures can help to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and that all data transfers are protected from unauthorized interception.
Regimented Vulnerability Management
The best managed services providers (MSPs) know that a regimented vulnerability management program is essential to keeping their clients’ networks secure. By regularly scanning for and patching vulnerabilities, MSPs can help prevent attacks before they happen.
But what exactly does a good vulnerability management program look like? In this blog post, we’ll share some best practices for MSPs to follow when it comes to vulnerability management.
1. Perform regular scans.
MSPs should perform regular scans of their clients’ networks to identify any potential vulnerabilities. These scans should be scheduled on a monthly or weekly basis, depending on the client’s needs.
2. Patch vulnerabilities promptly.
Once a vulnerability has been identified, it’s important to patch it as soon as possible. This will help prevent attackers from exploiting the vulnerability and gaining access to the network.
3. Keep track of all vulnerabilities.
MSPs should keep track of all vulnerabilities that are found, even if they’ve been patched. This will help the MSP identify any trends in attacks and make sure that all potential vulnerabilities are being addressed.
4. Educate clients on good security practices.
Disaster Recovery And Data Immutability
MSPs often talk about the importance of having a good disaster recovery plan, but what about data immutability? Data immutability is the concept of making sure that data cannot be changed once it has been written. This is important for many businesses, especially those in regulated industries. Having a plan for disaster recovery is one thing, but if your data can be easily changed, it is not worth much.
There are many benefits to having data that cannot be changed. For one, it provides a record that cannot be tampered with. This can be useful in legal situations or when auditing your own company. Additionally, it can help prevent data loss in the event of a disaster. Even if your primary storage system is destroyed, you will still have a copy of your data that cannot be modified.
There are several ways to achieve data immutability. One common method is to use cryptographic hashes. A cryptographic hash is a mathematical function that takes an input and produces a unique output. Once the data has been hashed, it cannot be changed without changing the output. This makes it very difficult for someone to maliciously modify your data.
Another option is to use blockchain technology. Blockchain is best known
Alert Monitoring And Minimal Access
Managed services providers (MSPs) have long been in the business of monitoring and managing client networks, but with the rise of cloud computing, there is an increased focus on alerting and minimal access. In this post, we’ll take a look at some best practices for alert monitoring and minimal access in the context of managed services.
Alert Monitoring
Alert monitoring is a critical component of any managed services agreement. MSPs must be able to quickly and easily identify when something has gone wrong on a client network. The most effective way to do this is to implement a centralized monitoring solution that can provide visibility into all aspects of the network.
There are a number of different software solutions available that can be used for alert monitoring. MSPs should evaluate their options and select a solution that meets their specific needs. Once implemented, the monitoring solution should be configured to send alerts to the MSP’s support team as soon as an issue is detected.
Minimal Access
Another important consideration for MSPs is ensuring that they have minimal access to client networks. This means having only the necessary level of access to perform their duties and nothing more.