Security Essentials and Tips
Security Risk Assessment: Assess risk first in order to justify appropriate technical solutions and policy/procedure updates.
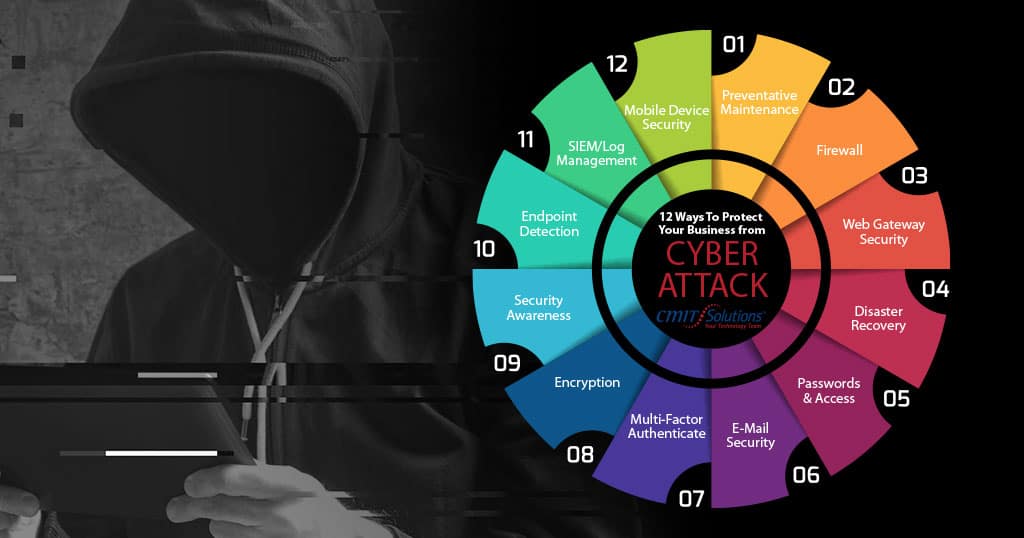
1. Preventative Maintenance
Employ automated patching to keep software updated for better security, schedule forced reboots of computing devices to ensure patches are effectively deployed, and continuously monitored for AV software definition updates.
2. Firewall
Employ a unified-threat management device with intrusion detection and prevention features. Determine if log management, alerting, retention, and threat remediation is necessary for compliance.
3. Web Gateway Security
Internet security is a race against time. Cloud-based security detects web and email threats as they emerge on the internet and blocks them on your network before they reach the user.
4. Data Backup, Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Services
Follow the Rule of 3–have critical files saved and recoverable from 3 locations. Employ the right DR/BC solution that meets the recovery time objective dictated by your business needs and ensure the solution is tested regularly.
5. Passwords and Access
Apply security policies on your network. Examples: deny or limit USB file storage access, enable enhanced password policies, set user screen timeouts, and limit user access.
97% of breaches could’ve been prevented with today’s technology
81% of all breaches happened to small and medium-sized businesses
1 in 5 small businesses will suffer a cyber breach this year.
6. Email Security Services
Most attacks originate in email. Reduce spam, filter for malware, protect against accidental deletion and archive for compliance.
7. Multi-Factor Authentication
Utilize MFA whenever you can to add an additional layer of protection to ensure that even if your password does get stolen, your data stays protected.
8. Encryption
Whenever possible, the goal is to encrypt files at rest, in motion (think email), and on mobile devices. Determine where encryption technology needs to be employed.
9. Security Awareness
Train your users- often! Employ a web-based training and phishing simulation tool that has granular reporting about user behavior to identify your weak links so that custom training plans can be executed.
10. Advanced Endpoint Detection & Response
Real-time SOC (security operations center) monitoring detects suspicious activity and network intruders and then rapidly responds with protocols to stop and remediate active threats that prevent damage from spreading, such as with ransomware attacks.
11. SIEM/Log Management
(Security Incident & Event Monitoring) Uses artificial intelligence to monitor all event and security logs from covered devices to protect against advanced threats. Also includes the reporting and log retention needed to meet compliance requirements.
12. Mobile Device Security
Today’s cybercriminals attempt to steal data or access to your network by way of your employees’ phones and tablets. They’re counting on you to neglect this piece of the puzzle. Mobile device security closes this gap.
BONUS! Cyber Liability Insurance
If all else fails, protect your business from financial loss and liability that results from a data breach or other cyber event.