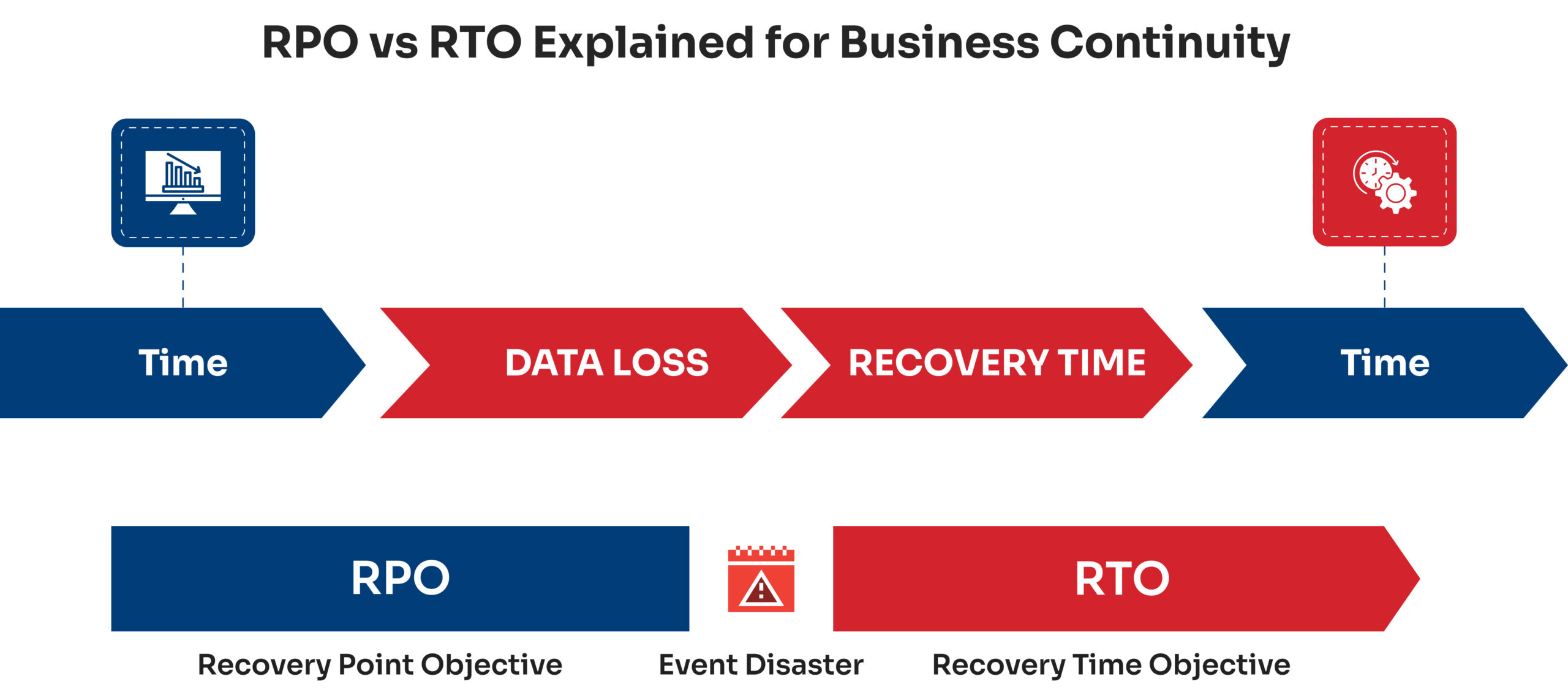
The answer lies in two crucial metrics for business continuity and disaster recovery:
1. Recovery Point Objective (RPO) — The maximum acceptable data loss, measured in time, and dictates your backup frequency.
2. Recovery Time Objective (RTO) — The targeted duration for restoring systems after a disruption, representing your maximum tolerable downtime.
Therefore, for your business to minimize data loss and downtime, you need well-defined RPO and RTO targets — supported by reliable data recovery services that can meet these objectives. A clear understanding of these metrics enables you to make informed risk management decisions.
Consider this: why address downtime now? If you underestimate its impact, think again: it leads to lost revenue, erodes trust, and damages your reputation.
Understanding these RTO and RPO is the first step toward building a business continuity strategy that truly protects your operations and your bottom line.
Exploring the Role of RPO and RTO for Business Continuity
RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss measured in time, answering the critical question: “How much data can we afford to lose?” For example, can your business afford to lose one hour’s worth of data?
A well-designed data recovery plan reduces or prevents potential data loss for a business during a disaster or outage. It sets backup frequency to ensure data loss stays within business limits. For example, an e-commerce RPO of one hour means you’d lose orders from only that period. This matters because data drives decisions, and losing too much impacts operations.
RTO focuses entirely on speed, addressing: “How fast do you need to recover?” In other words, can your data be restored within four hours? Can your systems be restored within this deadline? Consider this retail scenario: an RTO of four hours demands that your point-of-sale system recover within that window to prevent customer loss and sales disruption.
Now, the next question striking the mind would be: what is the difference between RPO and RTO? RTO minimizes downtime by accelerating system restoration, while RPO prevents excessive data loss through backup timing. They work together in disaster recovery planning. The urgency for data preservation (RPO) enables faster recovery execution (RTO).
Shorter RPO and RTO targets typically require greater investment. Therefore, balancing these objectives with resources becomes essential. Organizations often tier their applications by criticality to manage this — a strategy we’ll explore later.
Also Read: IT Roadmap: The Overlooked Strategy Slowing Down Growth
How Do You Calculate the Cost of Downtime for a Business?
Commence by quantifying the revenue impact of downtime through lost sales and employee productivity loss. These metrics highlight the direct financial hits that can cripple operations and help answer how long can a business afford to be down.
At the same time, let’s also not forget that extended outages also trigger reputation risk. They can damage your brand and erode customer trust through devastating indirect costs. Therefore, failing regulatory compliance during disruptions risks legal penalties or fines.
The formula sums up to:
Total Downtime Cost = Lost Revenue + Lost Productivity + Recovery Costs + Intangible Losses
In disaster recovery planning, measuring RPO and RTO proves critical for balancing data preservation and recovery speed. A business impact analysis leverages these metrics to prioritize recovery efforts, helping you select optimal data recovery based on system criticality.
Remember, setting RPO/RTO goals isn’t just about saving data — it’s about saving your business from existential threats. Therefore, don’t forget the human element. Train employees and provide communication tools to maintain productivity during interruptions.
Ultimately, defining your downtime and data loss tolerance through RPO/RTO targets builds true resilience for business continuity — and remember, not all systems need equal protection, which we’ll explore next.
Prioritize Your Recovery Efforts for Smart Investment
When determining how long your business can afford to be down, here’s the critical insight most leaders miss: Not all systems need the same recovery speed.
To balance RPO and RTO for business continuity, categorizing applications simplifies workload assignment into SLA Tiers aligned with business priorities.
- Tier 1: Mission-critical applications directly impact revenue or customer experience (e.g., transaction systems, CRM), requiring stringent RPO and RTO targets supported by robust data recovery services — such as a 2-hour RPO and 1-hour RTO. Achieving these stringent targets necessitates robust data recovery services.
- Tier 2: Important applications support core operations with less immediate operational impact (e.g., payroll, collaboration tools), needing moderate targets like a 12-hour RPO and 6-hour RTO.
- Tier 3: Less critical applications have minimal short-term business impact (e.g., desk booking systems), tolerating lenient targets such as 24+ hour RPO and end-of-day RTO.
By aligning your disaster recovery plan with application criticality, you optimize budget allocation while ensuring priority systems receive focused attention — a hallmark of strategic IT solutions.
Therefore, concentrate investment where it safeguards Key Performance Indicators like revenue by prioritizing Tier 1 applications. With your systems tiered, you’re prepared to build a step-by-step continuity plan, minimizing downtime and data loss for businesses — our next focus.
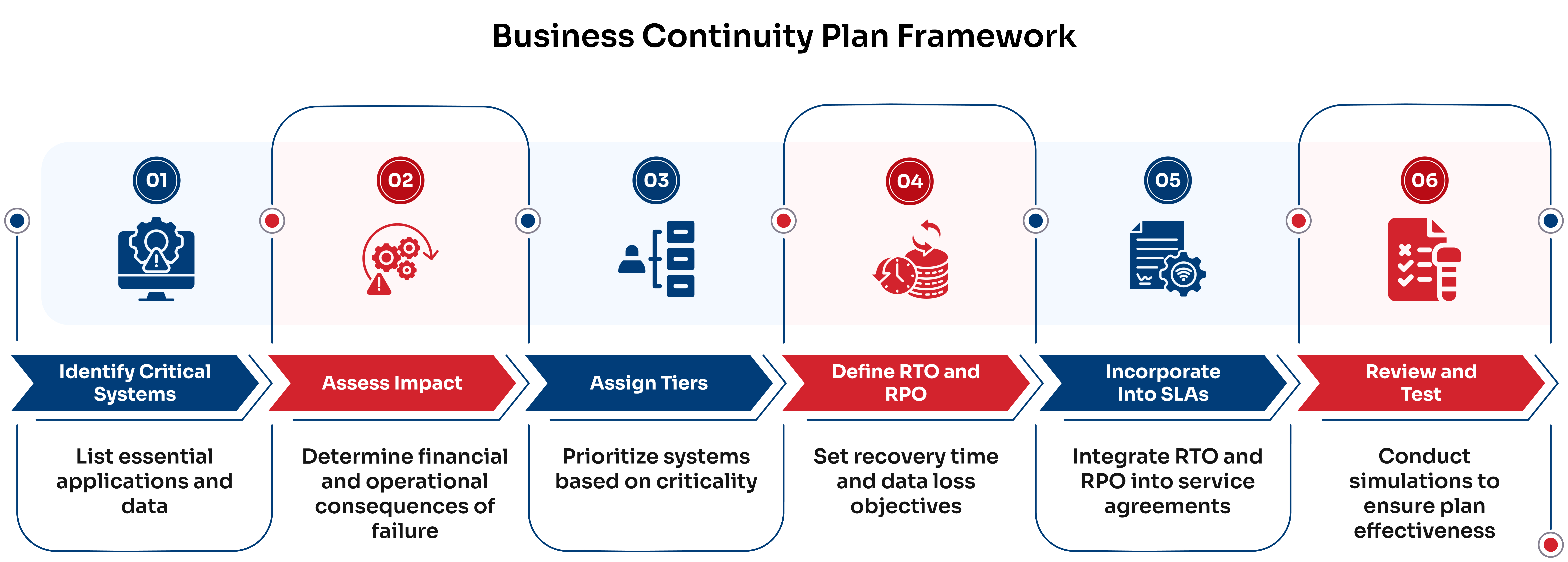
A Practical Framework for Your Business Continuity Plan
Here’s a stepwise roadmap from CMIT experts to ensure business continuity:
- Step 1: Start by identifying and listing your business-critical applications and data, such as CRM or inventory systems, since this forms the foundation of your business continuity plan.
- Step 2: Next, for each critical system, determine the financial impact (like lost revenue) and operational impact (like halted productivity) if they failed, as this assessment defines your recovery objectives.
- Step 3: Based on the business impact, assign a tier to each system — Tier 1 for mission-critical and Tier 2 for important — to prioritize recovery efforts.
- Step 4: Define realistic RTO and RPO for each tier, ensuring these targets align with your business priorities and risk tolerance.
- Step 5: Regularly review and test your business continuity plan through simulations to ensure alignment with evolving needs and consistent achievement of recovery objectives.
It’s essential to understand that RPO and RTO are business decisions, not just technical ones, directly answering how long your business can afford to be down and influencing potential data loss. Your defined RPO and RTO targets should be incorporated into Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with your IT team or provider, guiding the selection of data recovery.
Next, let’s explore how small businesses can apply these principles to enhance their RPO and RTO.
How Can a Small Business Improve Its RPO and RTO?
Steps small businesses can take include:
- Conducting a business impact analysis to identify critical systems and data
- Setting realistic RPO and RTO targets based on their budget and risk tolerance
- Implementing regular, automated backups and utilizing cloud-based recovery solutions for faster restoration
- Testing their disaster recovery plan
- Prioritizing critical applications and data for more frequent backups and faster recovery will also help optimize resources
By implementing this structured approach, you’re building a documented and resilient business continuity strategy that guards against unforeseen disruptions.
Make Business Resilience a Strategic Priority
Understanding and defining RPO and RTO is fundamentally a business leadership responsibility, not just an IT task. Strategic prioritization allows for effective protection without excessive cost so that you can safeguard critical operations efficiently.
Partnering with trusted providers like CMIT Solutions at Silver Spring, known for delivering comprehensive business IT solutions, can help you assess your current systems. With us, you make informed decisions to strengthen your continuity posture immediately by aligning precisely with your RPO and RTO, removing the guesswork in a crisis. This ensures your business isn’t just prepared on paper — it’s equipped with a data recovery strategy that delivers exactly when it matters most.
While our primary office is in Silver Spring, CMIT Solutions of Silver Spring is dedicated to delivering expert IT support, proactive cybersecurity, and reliable technology solutions to businesses throughout the region. This includes our valued clients in Rockville, Derwood, Chevy Chase, Olney, Burtonsville, and Highland. We’re committed to being your trusted IT partner for local businesses.