FAQs
1. What is the difference between data backup and disaster recovery services?
Data backup refers to the routine copying and secure storage of business data so it can be restored if lost, corrupted, or encrypted. Disaster recovery services go further by restoring entire systems, infrastructure, and operations after events such as ransomware attacks, hardware failure, or natural disasters. Together, data backup and recovery services ensure both file protection and full business continuity.
2. How do data backup and disaster recovery services protect against ransomware?
When ransomware encrypts systems, clean backup copies allow IT teams to remove the infection, rebuild systems, and restore data without paying attackers. Versioned backups, offline storage, and secure cloud replication reduce the risk of backup compromise and allow rapid recovery to a point before the attack occurred.
3. How often should business data be backed up?
Critical business systems often require continuous or near-real-time backups, while less sensitive data may be backed up daily or weekly. Backup frequency should be based on how much data loss a business can tolerate, known as the Recovery Point Objective, RPO.
4. What are cloud data backup solutions and are they secure?
Cloud data backup solutions store encrypted copies of business data in geographically separate data centers. Security is maintained through encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and redundant infrastructure, reducing risks associated with on-site hardware failure or local disasters.
5. Why is backup testing important for data resilience?
Backups are only reliable if they can be restored successfully. Regular backup testing verifies data integrity, confirms recovery procedures, and identifies configuration issues before a real incident occurs, reducing downtime during emergencies.
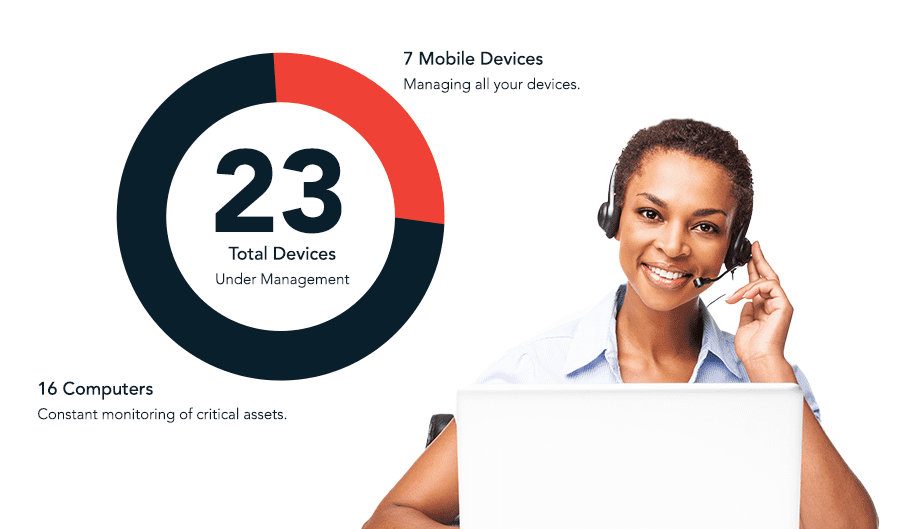
6. What does a data backup consultant do for a business?
A data backup consultant evaluates system risks, data criticality, compliance requirements, and infrastructure dependencies. They design structured backup strategies, define retention policies, and ensure that storage, recovery, and monitoring processes align with business continuity goals.
7. How do data backup solutions support regulatory compliance?
Many regulations require secure storage, retention policies, encryption, and audit trails. Professionally managed data backup solutions include timestamped version history, encrypted storage, and documented recovery processes that support legal, financial, and industry compliance standards.
8. Can a business operate during a disaster with proper backup systems?
Yes. Modern data backup and disaster recovery services often include cloud failover environments that allow employees to work remotely while primary systems are restored. This minimizes service interruption and protects revenue continuity.
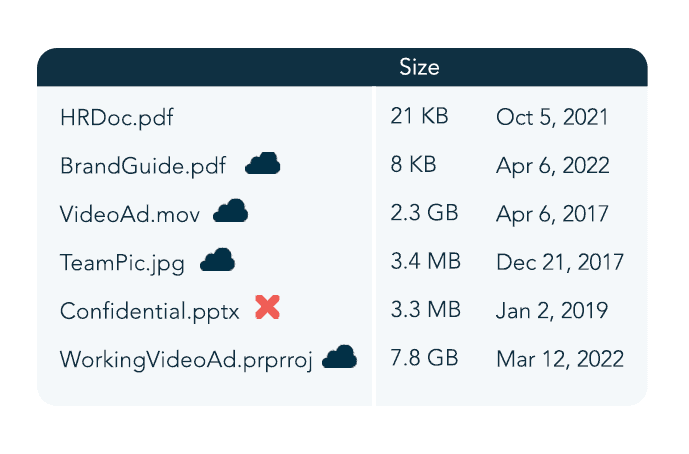
9. What types of data should always be included in backup plans?
Priority data typically includes financial records, customer information, operational databases, system configurations, emails, and application environments. Backup plans should cover both structured data and full system images.
10. How do layered backup strategies improve data protection?
Using multiple backup types, such as on-site image backups, off-site cloud copies, and immutable storage, reduces single points of failure. Layered backup strategies improve resilience against cyberattacks, hardware failure, and environmental disasters.